"To take hold skin infections need to penetrate the skin, which is the
largest and most visible organ of the body. The skin functions as an
anatomical barrier between the internal and external environment. As
such, it protects the body from pathogens (harmful organisms) and other
substances in the environment. Although there are millions of bacteria,
yeast and other microorganisms normally found in the human skin, skin
infections occur only when there is a disturbance in the integrity of
the skin or when the immune system is weakened. Below you will find pictures, descriptions and common treatment options for common bacterial and fungal infections."
 Skin infection on legs caused by Erysipelas, a form of celulitus. Appears after other symptoms such as joint pain,
fever and/or vomiting. Treated with oral antibiotics.
Skin infection on legs caused by Erysipelas, a form of celulitus. Appears after other symptoms such as joint pain,
fever and/or vomiting. Treated with oral antibiotics.Overview
Video: Common Skin Infections
Dr. Paul W. Bolin discusses the causes, symptoms and treatment of common skin infections.
 Infected skin abscess that is painful, tender and filled with pus. The skin infection needs to be drained via an incision. Antibiotics may be needed.
Infected skin abscess that is painful, tender and filled with pus. The skin infection needs to be drained via an incision. Antibiotics may be needed.A skin infection occurs when the skin is invaded by harmful microscopic organisms like viruses, bacteria, and fungi, where they multiply and cause subsequent tissue injury, which may progress to disease. A break in the skin, such as a wound increases one’s risk for a skin infection. Other factors, such as poor hygiene, presence of a systemic disease, or weakened immune system also increase one’s likelihood for acquiring an infection on the skin surface.
The most common causes of infection includes:
Viral Skin Infections
Viral skin infections are caused by diseases such as Herpes simplex virus (HSV), Varicella, Herpes zoster, Human papilloma virus (HPV), Chicken pox, the Pox virus (chickenpox) and Molluscum contagiosum.
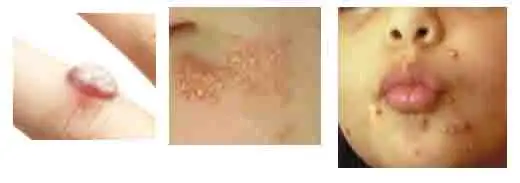 Common Types of Viral Skin Infections; Pictures left to right; wart, herpes virus, Molluscum Contagiosum
Common Types of Viral Skin Infections; Pictures left to right; wart, herpes virus, Molluscum ContagiosumChicken Pox Virus
Chicken pox is spread through the air (mucosal droplets). Patients are infectious 2 days prior and 5 days after a rash appears. Additional symptoms include sore throat, tiredness and cough. The papules tend to itch and after 2 days become crusted.
Severe cases cause respiratory symptoms. Treatment includes warm baths and calamine lotion. Adults receive oral anti-virals.
Herpes Virus
Herpes is a contagious infection. Lesions tend to recur in the same site. Lesions start as a red skin area, and then form a macula and then crusts to a papula or blister. If the blister is kept moist it can remain infectious.
HPV
HPV or Human papillomas virus infects that outer skin cells There are 100 types of HPV. The virus is transmitted through direct contact.
Signs of HPV include common warts that are found on the bottoms of the feet, on the fingers, knees and elbows.
Most viral warts heal without treatment.
Bacterial Skin Infections
Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes result in conditions such as impetigo, cellulitis and folliculitis as shown below.
 Pictures of Bacterial Skin Infections (Shown From Left to Right; Scalp Folliculitis, Impetigo)
Pictures of Bacterial Skin Infections (Shown From Left to Right; Scalp Folliculitis, Impetigo)Boils (Furunculosis) and Carbuncles
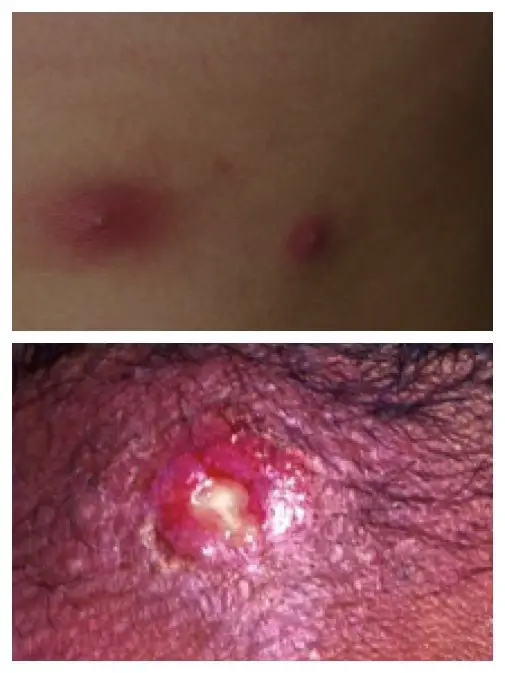 Bacterial Skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Both the infection on the chest which turned into Boils and the infection on the back of the head (Carbuncle) were caused by this bacterium.
Bacterial Skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Both the infection on the chest which turned into Boils and the infection on the back of the head (Carbuncle) were caused by this bacterium.Boils are round tender abscesses that are caused by a bacterial infection. A carbuncle is a inflamed mass on the head that contains the pus drainage from multiple hair follicles. A carbuncle is also an abscess.
Both are found in skin areas that contain hair follicles that are frequently exposed to perspiration and friction.
Both are usually caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. The conditions are treated with oral antibiotics. Abscesses may need to be drained or drainage may be helped by use of a warm compress placed on the skin lesion.
Cellulitis
 Cellulitis Bacterial Skin Infection is a Deep Skin Infection that is Treated with Antibiotics. It can Occur at Any Age. Open Wounds Can Spread with Direct Contact. Source: Meisenheimer Clinic
Cellulitis Bacterial Skin Infection is a Deep Skin Infection that is Treated with Antibiotics. It can Occur at Any Age. Open Wounds Can Spread with Direct Contact. Source: Meisenheimer ClinicCellulitis is caused when a wound (insect bite, cut, abrasion, puncture wound) makes it possible for an infection to enter the skin. It is frequently found on the leg and can cause lymph node swelling (lymphangitis).
Cellulitis can also occur where there is a preexisting skin infection. Erysipelas (see picture below) affects the face and lower extremities. It s a bright red skin infection that is painful, and has a sharply defined area when seen against normal skin. Before the infection appears the patient may experience vomiting, joint pain, headache, fever and chills.
Treatment involves the use of antibiotics and keeping the leg elevated.
 Bacterial skin infection picture of Erysipela, a type of cellulitis. Infection on face that causes the skin to be raised due to dermal lymphatic involvement.
Bacterial skin infection picture of Erysipela, a type of cellulitis. Infection on face that causes the skin to be raised due to dermal lymphatic involvement.Ecthyma
Ecthyma are ulcerated infectious lesions that extend through the skin. They may form a scar after healing. The cause is either Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
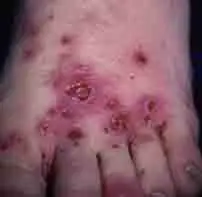 Skin infection on foot resulting in Ecthyma which is caused by a bacterial infection. It has a "punched out"
appearance.
Skin infection on foot resulting in Ecthyma which is caused by a bacterial infection. It has a "punched out"
appearance.Folliculitis
 Genital folliculitis picture that could be accompanied by a yeast infection on the skin.
Genital folliculitis picture that could be accompanied by a yeast infection on the skin.Folliculitis is a bacterial infection that occurs in the hair follicles. The pustules are itchy and are less than 5mm in size. It can occur anywhere on the body where there is hair.
Genital folliculitis may be sexually transmitted. It can be accompanied by the yeast infection on skin called candidiasis (fungal infection).
Most cases of folliculitis are caused by the bacteria Staphyloccus aureus. Causes include exposure in a swimming pool or hot tub.
The condition is treated with anti-bacterial soap, topical ointments or creams, or oral anti-staphylococcal medications.
Impetigo
 Impetigo pictures that show the bacterial skin infection on face that show the characteristic honey colored skin crust.
Impetigo pictures that show the bacterial skin infection on face that show the characteristic honey colored skin crust.Impetigo (impetigo contagiosum) is a bacterial skin infection frequently seen in children age 2 to 5. It can appear in individuals of any age.
Skin lesions have a characteristic "honey" color and look like a crusts. There is a form found in younger children that includes skin bullae which are raised bumps that are filled with a clear yellow fluid. When the bullae rupture they leave behind a thick brown crust Bullae are found in the diaper area, legs, arms and face.
It is highly contagious through close contact.
MRSA
MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) is a bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics. It can cause problems such as skin infections.
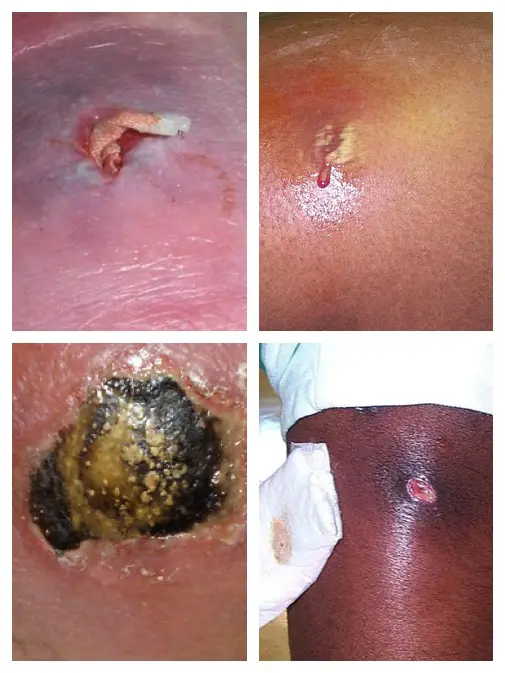 MRSA pictures of anti-biotic resistant skin infections. Photo Credits: CDC, Gregory Moran, M.D. (bottom left), Major Kirk Waibel, MD (top left)
MRSA pictures of anti-biotic resistant skin infections. Photo Credits: CDC, Gregory Moran, M.D. (bottom left), Major Kirk Waibel, MD (top left)Fungal Skin Infections
Fungi or yeast cause bacterial skin infections such as Onychomycosis, Trichophyton rubrum, Candida albicans, Malassezia furfur, athlete’s foot, jock itch, Ringworm, and Tinea versicolor.
 Picture of Common Fungal Skin Infections (Shown Left to Right; Athletes Foot, Jock Itch, Tinea Versicolor)
Picture of Common Fungal Skin Infections (Shown Left to Right; Athletes Foot, Jock Itch, Tinea Versicolor) Source: Meisenheimer Clinic
Athlete's Foot (Tinea Pedis)
 Athlete's Foot Pictures
Athlete's Foot PicturesTinea Pedis is a fungal skin infection found on the feet. Athlete's foot is frequently contracted in moist public places such as a gym shower. The fungus does well in moist, warm, skin areas.
Symptoms of athlete's foot include redness and scaling between the toes.
Athlete's foot is treated with a Clotrimazole or Miconazole cream 2x daily for 4 weeks. Over the counter treatments such as Lotrimin are effective. If your case does not respond see a Doctor.
Jock Itch (Tinea cruris)
Jock itch is a fungal infection of the groin. There are several types of fungus that cause the infection.
Treatment requires a topical anti-fungal such as Lotrimin used for a period of 4 to 6 weeks. If the infection does not respond to treatment a prescription oral antifungal may be needed. Oral medications are taken for 1 to 2 weeks.
Ringworm (Tineae Corporis)
 Ringworm picture on leg.
Ringworm picture on leg.Ringworm is a skin fungal infection that is usually seen on the chest, arms and legs. Symptoms include itch and the characteristic round shape.
Onychomycosis
 Nail fungal infection.
Nail fungal infection.Onychomycosis is a fungal infection found in the nailbeds. It often starts as athlete's foot and then moves to the nails. It doesn't respond well to topicals.
Oral antifungals are frequently prescribed to treat Onychomycosis.
Diagnosis
To identify the pathogen causing an infection, a clinical skin examination is initially done, followed by laboratory examination of specimens obtained from skin scrapings, pus or exudates (fluid from the lesions). Microscopic examinations may involve the use of staining techniques and culturing methods to identify microorganisms. Ultraviolet light (Wood's lamp) or KOH fungal culture test may also be used for fungal infections.
Symptoms
Most types of infection are characterized by erythema (redness), edema, and other signs and symptoms of inflammation. These may include itching, scaling, and pain. Focal accumulation of pus or fluid may develop. Alternatively, there may be no signs of inflammation. Other appendages of the skin such as the nails and hair follicles may be affected, causing discoloration and thickening of nails, inflammation of hair follicles and hair loss.
Infection may be localized or widespread, depending on the cause, and symptoms may vary from an inflammation confined to a small area of the skin or may involve the rest of the body, causing fever, malaise and inflammation of lymph nodes.
Treatment
Local infections on the skin are treated by repeated cleansing using soap or detergent, which contain an antimicrobial agent. Topical antiseptics like chlorhexidine may be used to eliminate the source of infection and prevent its spread to adjacent skin area or to other individuals.
Drying agents like aluminum chloride may be used to inhibit the overgrowth of other opportunistic microorganisms.
Keratinolytic agents like topical salicylatesare used to remove thick skin lesions that may harbor pathogens and to expose the infected skin surface to other local treatments.
Topical antimicrobial agents (antibiotics, antiviral and anti-fungal agents) are often used, but systemic therapy (oral or injected) may be needed for patients with more extensive skin disease.
Natural Remedies
Natural Remedies for Viral Infections on the Skin:
Molluscum Contagiosum Remedy: This Molluscum Contagiosum Remedy is made from 100% plant extracts. The product is applied to the skin 2x to 3x per day until the infected area is clear. This product helps to relieve the symptoms without using acids or chemicals found in other products. (source:Markum E, Baillie J (2012). "Combination of essential oil of Melaleucaalternifolia and iodine in the treatment of molluscumcontagiosum in children". J. Drugs Derm. 11 (3): 161–165)
Wart Removal:
Wart Remover: A wart forms when a virus enters a small cut or wound on the body. The Naturasil Wart Remedy uses plant extracts to help dry up warts so that they flake away. The treatment is applied 3x to 4x times per day until the wart disappears. You should see progress in 3 to 6 weeks using this method.
Natural Remedies for Fungal Skin Infections:
Jock Itch Remedy: Phytoseptic for Jock Itch Remedy: Formulated with natural plant extracts to treat jock itch. Results are achieved in 1 to 2 weeks.
Athlete’s Foot Remedy: This Athlete’s Foot Remedy is formulated to reduce the discomfort associated with Athlete’s foot and to assist with the elimination of the fungal infection.
Tinea Versicolor: The Tinea Versicolor Remedy helps to eliminate the fungal infection on the skin surface and by penetrating the skin. It assists in relief of tinea versicolor including candida and onychomycosis. The product is made from 100% plant extracts. Product is applied 2x to 3x per day until the condition clears.
Brochures
by: Zara Jaulim MRCP, Nicola Salmon MRCP and Claire Fuller MA, FRCP
References
Cevasco, N. and Tomecki, K. Common Infections. Cleveland Clinic.
Aly, R. Microbial Infections of Skin and Nails. NCBI.
American Academy of Dermatology
