" Genital scabies tends to be classified as a sexually transmitted disease, although there are ways to contract scabies other than through sexual intercourse. It is found in women and men. More than 300 million cases of scabies occur every year and affect everyone, in every walk of life. Personal hygiene has nothing to do with whether or not you may contract scabies. The mites are found in the genitals or pubic area, hands, under the arms, webs of the fingers, on the breasts, elbows, wrists, feet, scrotum, aureola of the breasts. around the nipples and on the buttocks. Mites can live for 72 hours outside of the body, making it easier for them to spread via towels or bed linen. When they find a human host they burrow under the skin. Symptoms include itch that worsens at night or after bathing/showering, tiny rash spots or inflamed or raw broken skin. You might see lines where the mites have burrowed into the skin. Treatment involves the use of topical lotions that are prescribed by a Doctor of that are available over the counter. It can take several weeks of treatment for the itching to stop. Sex should not resume until treatment has ended to avoid transmission to another person."
 Genital scabies pictures on the penis (see blue arrows).
Genital scabies pictures on the penis (see blue arrows).Source: Nodular Scabies of the Genitals (1)
Causes of Genital Scabies
Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment of Genital Scabies
Dr. Paul W. Bolin on the diagnosis and treatment of genital scabies. Includes pictures.
There is only one cause of genital scabies and that is the Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis, also referred to as the Human itch mite or Scabies itch mite. It’s a very small and nasty, eight-legged round bodied bug, just barely visible to the eye. Additionally, since these creatures furrow under the skin and create tunnels to lay eggs, it’s hard to pin point the cause of your itching unless you see a doctor.
The scabies mite continues to burrow for about 10 days while eating your flesh while dropping 3 to 4 eggs per day. Once she runs out of eggs she dies. Once the eggs hatch after a few days, the newly born mites use the burrow and crawl out of the skin and stay on the skin in a hair follicle. These larvae then molt and grow. After 3 cycles, they are adults. The males will migrate out of the hair follicles and will look for females to sexually reproduce. Once they find females, they sexually reproduce and the female will then migrate out of the hair follicle and look for a location to burrow into your skin. The lifespan and reproductive cycle is 10 to 14 days.
How Do You Get Genital Scabies?
You get scabies through close contact with another person through body or sexual contact. Mites can also be contracted from bedding or other surfaces where mites can remain alive for 72 hours.
Does Scabies Affect Fertility?
Scabies does not affect fertility.
What Are The Symptoms?
 Scabies nodules pictures - classic "s" shaped burrow or tunnel picture. It is 1 centimeter long and contains the mite eggs.
Scabies nodules pictures - classic "s" shaped burrow or tunnel picture. It is 1 centimeter long and contains the mite eggs.Genital scabies have a wide variety of signs and symptoms that should alert the infected person that something is not right. For instance, you may or may not see a small zigzag or "s" shaped blister on your genitals, around the penis or vagina, or other parts of your body – usually the moist parts, because scabies mites love warmth and wetness. The blister is the female’s trail, as she is laying her eggs under your skin.
Itching can cause the scabies to move from one skin area to another.
 Genital Scabies Picture that shows Scabies symptoms on genital area such as irritated skin, pimples, mite burrows and rash.
Genital Scabies Picture that shows Scabies symptoms on genital area such as irritated skin, pimples, mite burrows and rash.Source: CDC/ Susan Lindsley
The most obvious signs of the scabies condition are the intense itching, more so at night, and the tell tale red rash from the mites secretions and scratching.
As for the severe itch you get with genital scabies, the reason for that is due to the secretions the mite oozes into your skin. As the female is snuggling in to start eating, she produces irritating secretions, as she lays her 1-4 eggs per day, that will give you an allergic reaction.
Burrows tend to be "s" shaped or a little bit of a curve.
Once the eggs hatch, they head for the
skin’s surface, where the females start their own tunnels and burrows
and produce more irritating secretions. Other mites stay on the surface
of the skin in shallow pockets and also make more of the fluid causing
your allergic response. This explains why the itch gets worse over time
and why it does not stop.
If a doctor is not consulted at this stage, the skin may begin to crust over or get scaly. Skin reactions are called erythematous papules. This is not a good sign and the crusts often harbor literally millions of mites and their eggs. By that point, genital scabies is very hard to treat. Watch for the early harbingers of scabies in the genitals by looking for little red bumps that may look like hives, spider bites or pimples. If these unexplained bumps are also in your armpits, under your nails, at the belt line, between your fingers, the buttocks, in the elbow crease, the inner thighs, on wrists, under watches and rings or around the nipples in women and on the penis for men, there is a good chance you are dealing with scabies.In children, look for signs in the scalp, palms of the hands or soles of their feet. For scabies in babies, you will typically see head and neck involvement. Be aware that a bacterial infection may set in if any of the skin lesions does get infected. This tends to happen more often with children than adults, but may also happen if an adult scratches until they set up the right environment to cause an infection.
 Picture of Genital Scabies 32 year old man developed scabies on arms, wrist, legs, abdomen
Picture of Genital Scabies 32 year old man developed scabies on arms, wrist, legs, abdomenSource: Clemens Esche, MD, DermAtlas
Diagnosis
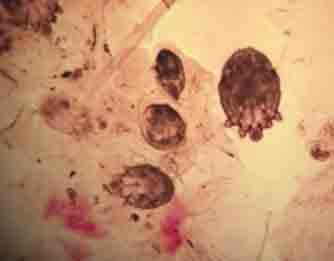 Magnified view of scabies on genital after skin scraping in Doctors office.
Magnified view of scabies on genital after skin scraping in Doctors office.When dealing with scabies, it is hard to diagnose on sight and thus the doctor will do a couple of things to determine if you are infected. The first test usually involves swabbing an inflamed area with sterile mineral oil and then taking a skin scraping. The physician will be able to see the mites, eggs and feces under the scope.
The other test is an ink test, which is using a black or blue felt-tipped pen on the suspicious areas of infection. The skin is inked then wiped clean. Typically, once the skin is cleaned off, the mite’s burrows under the skin may be seen, enabling the doctor to diagnose scabies.
Diagnosis has also been aided by tools such as the epiluminiscence microscope and video-dermatoscopy.
If you come in contact with someone that has scabies, you may not immediately develop any symptoms.
What Is The Treatment?
The treatment for genital scabies is Permethrin 5% cream. You cannot get it over the counter. Do not use lice OTC medications since it does not have the same strength. Creams are applied to the entire body from the neck down because the scabies can be anywhere. It is rinsed off after 12 hours.
There is another treatment available called Lindane 1% lotion. There are dangerous side effects such as seizures which is why Permethrin is preferred, even though Lindane is more effective. Lindane is only used if Permethrin doesn't work.
The body cannot fight off scabies on its' own since the scabies burrow is superficial on the skin.
If the condition is not treated quickly, the female mite will lay eggs for up to five weeks. Scabies is highly contagious and you may contract it through close contact with someone who has this mite infestation. They can be transferred by holding or shaking hands, sleeping together or using the same towels or bedding as an infected person and of course sexually.
All linen, towels and clothes should be washed on the hot water cycle to kill any mites.
If blankets and towels are shared in the household then more than one family member may need to be treated. Family epidemics are common.
Can Scabies be Treated When Breastfeeding or Pregnant?
Yes, but not all treatments may be appropriate. See a Doctor. Some creams such as Permethrin can be used under a Doctors directions.
Does Scabies Cause Cervical Cancer?
There is no known link between cervical cancer and scabies.
Natural Remedies for Scabies
Natural treatments exist such as, mixing 1 tsp of hot water and 5 drops of Bergamot. Cool and apply. Use two to three times daily.Try mixing 5 drops of Lavender Oil, Thyme Oil and Peppermint Oil, then mix with 2 Tbsp vegetable oil. Massage into the affected area once a day.Add one part Resinall K (Chinese herbal formula for pain, swelling and skin disorders) to 3 parts warm water.
We do not recommend scabies home remedies
Prescription Scabies Treatment
Prescription treatment approaches involve the whole body, except the head and neck (usually, unless it’s a child or baby with scabies.) Everyone in the family will need to be treated. Unlike the natural remedies for scabies described above, the most popular medicinal treatments are permethrin, malathion, sulfur and benzyl benzoate emulsion. These are all poisons and need to be handled with extreme care, particularly if you are treating children. Always follow your doctor’s instructions to the letter when using toxic chemicals.
Protection
To protect yourself from genital scabies use a condom. Avoid sharing sex toys or rubbing against an infected person without covering the genitals.
Wash all blankets, linen and towels in hot water to kill any scabies mites that are not on a human host.
Brochure
References
(1) Nodular Scabies of the Genitals
Virendra N. Sehgal, Shalini Malhotra and Venkatesh Ramesh
(3) Scabies - Center for Young Women's Health
Boston Hospital
