"When
a hair follicle is damaged, a type of skin abscess can form, allowing
folliculitis causes such as bacteria (usually Staphylococcus
aureus) and fungus to
enter the skin. Hair follicles are damaged by anything that
can
irritate or damage the skin such as shaving, a skin scrape or clothing
that rubs against the skin. The condition is referred to by several
names based on the cause and area of the body affected. This
includes Pseudofolliculitis barbae (bacterial folliculitis
that occurs after shaving or when the beard hair curls into the skin),
Tinea barbae (caused by a fungus), Barber's
itch, hot tub folliculitis or hot tub dermatitis. In cases where there
was exposure to water, it occurs under the bathing suit, such as on the
chest and rear/buttocks several hours to five days after being exposed
to the bacteria.
Folliculitis symptoms include the
appearance of a white follicle or pimple located at the base of one or
more strands of hair. It can occur anywhere on your skin and
can be painful. The infection may be just on the skin surface
or in more chronic cases, penetrate into deeper skin layers.
Cases caused by water such as hot tub folliculitis will
usually heal
with no treatment. Other forms that are only on the surface of the skin
can be treated with topicals applied to the skin and antibacterial
soaps. Infection that penetrates deeper into the skin will require oral
antibiotics. Individuals that frequently contract
folliculitis may require frequent use of anti-bacterial soaps and
shampoos to control the condition."
 Folliculitis Pictures on Buttocks and Neck. Common causes include irritation from shaving, clogging pores with greasy skin products, medications such as steroids or products with coal tar, bacterial or yeast infection or immunosuppression from diseases such as HIV.
Folliculitis Pictures on Buttocks and Neck. Common causes include irritation from shaving, clogging pores with greasy skin products, medications such as steroids or products with coal tar, bacterial or yeast infection or immunosuppression from diseases such as HIV.Source: New Zealand Dermatological Society (DermNet) via a Creative Commons License
Folliculitis Causes
Video: Folliculitis Causes and Treatment
Dr. Ricardo Mejia discusses what is folliculitis and how it is treated.
Ever been to the hairdresser or barber and they use a razor on the back of your neck making you itch uncontrollably for days afterwards? Join the club. The itch may be folliculitis and is the result of many things, including friction from your clothes, shaving or the blocking of a follicle. Folliculitis typically gets infected by staph bacteria or Pseudomonas (bacteria) as well.
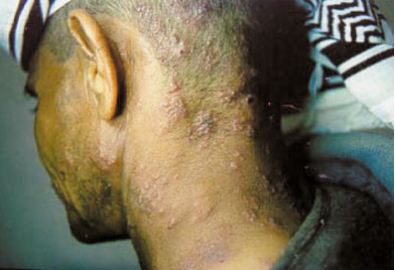 Folliculitis is commonly seen on the scalp, resulting in pus filled abscesses. Source: Principles of Pediatric Dermatology
Folliculitis is commonly seen on the scalp, resulting in pus filled abscesses. Source: Principles of Pediatric DermatologySuperficial Folliculitis
As mentioned, there are several types of superficial folliculitis causes (also called Bockhart impetigo). Superficial refers to the conditions which do not penetrate deeply into the skin.
These include:
- Staphylococcal folliculitis: this is the most common type of bacterial folliculitis. In children it occurs on the scalp, and in adults the condition can occur in any hairy area. When in the beard it is called Barber's itch. Symptoms include itch and puss filled abscesses that cause skin bumps. It usually occurs around the bearded area of a man’s face, and the upper lip. If you have this condition it's not a good idea to shave, as this only makes thing a lot worse.
- Hot tub folliculitis (pseudomonas folliculitis): Folliculitis can be caused by exposure to bacteria in a heated pool such as a whirlpool or hot tub. This type of folliculitis is referred to as either hot tub dermatitis or hot tub folliculitis. It is caused by bacteria that colonize in hot tubs and whirlpools that are not properly chlorinated. This type results in rash filled with skin bumps. The rash will itch, with the worst rashes appearing under areas which were covered by a bathing suit
- Tinea barbae: Tinea barbae is a close cousin of barber’s itch, but is caused by a fungus. It is most often seen in beards, with the skin area that surrounds the beard becoming red. The skin abscesses are also filled with puss. other symptoms can include fever. The lymph nodes may swell as well.
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae: This is a condition where the beard hairs curl into the skin causing irritation. It can result in scaring on the man's face and also the neck. Pseudofolliculitis barbae usually affects men with darker skin. What happens is, if curly beard hairs are shaved off too short, they may curl back into the skin, causing inflammation. There may or may not be a skin infection with the irritation.
- Pityrosporum folliculitis: This is one of the folliculitis causes in teens and men that is triggered by a fungus. Symptoms primarily appear on the chest and back. It can also appear on the face, upper arms, shoulders and neck.
- Herpetic folliculitis: When a cold sore is cut during shaving, a blister can form which is triggered by the herpes simplex virus. The virus can spread to hair follicles.
Causes of Deeper Folliculitis
In deeper folliculitis, the folliculitis penetrates deeply into the hair follicles (called perifolliculitis). Deep folliculitis can result in crusted lesions, and scars (cicatricial alopecia).
- Gram negative folliculitis: Anti-biotic can affect the bacteria in the nose, resulting in more bacteria being allowed to colonize than normal. Bacteria can spread to the face, resulting in acne lesions.
- Skin Boils: When a folliculitis infection penetrates deeply into the skin, boils can form in the shape of a pink or red bump. As puss accumulates under the bump, it can get larger and break. Several boils in a group are referred to as a carbuncle (appear on the thighs, back, shoulders, neck). A carbuncle can result in a scar. in addition to prescription medications, healing can be supported with a natural remedy such as Boil-RX.
- Eosinophilic folliculitis: This is one of the folliculitis causes, particularly in people with HIV. Symptoms include patches of skin sores/puss filled abscesses and itch. it may change the skin to a darker color.
 Eosinophilic Folliculitis Pictures
Eosinophilic Folliculitis Pictures Folliculitis on Upper Arms Caused by Medications such as Steroids (Acneiform Folliculitis)
Folliculitis on Upper Arms Caused by Medications such as Steroids (Acneiform Folliculitis)Folliculitis vs. Acne
Acne is frequently confused with folliculitis or seen at the same time. Folliculitis should be considered in cases where there is a limited response to acne. Ask a Dermatologist to do a KOH test to see if papules and pustules are being caused by yeast. Treatment involves stopping oral antibiotics and moving to a combination of topical and oral anti-fungal treatment. Topicals can also be used for the acne.
Pictures of Genital Folliculitis Symptoms
 Folliculitis Pubic Area Pictures
Folliculitis Pubic Area PicturesSymptoms
The most common symptoms may include itching, a red rash and either pimples or pustules near hair follicles on your groin, neck or even genital area. On the head, white pustules appear at the base of each hair. Depending on how much you scratch and how bad your infection happens to be, the pimples may even crust over. Folliculitis may affect 10%-20% of people at some point in their lives.
It may start out as multiple tiny red or even pink bumps at the base of your hair follicles. You might think it looks a bit like chicken skin in coloration and have a pebbly feel. Some of the bumps may have a red halo around them, which indicates inflammation. You may find it anywhere on your body, and that will include your cheeks, legs, arms, buttocks, back and chest. It does not affect the soles of your feet, your eyes, mouth, or palms.
If you scratch the tops off the bumps, you may see a hair trapped inside, which is turning back into the skin and causing the inflammation and itching. You may also have acne whiteheads at the same time. It doesn’t really matter how old you are, as just about anyone can get folliculitis.
There are however, some groups that are more susceptible to folliculitis, including, diabetics, people with compromised immune systems, people taking immune-suppressing drugs, those with cancer, chronic illnesses and those undergoing chemotherapy.
Diagnosis
Usually, the doctor only needs to see how your skin looks. However, there are a number of other conditions that also “look” like folliculitis. To differentiate the condition from other possible causes the Doctor may recommend tests such as a skin biopsy or skin bacterial culture. Some of the other conditions that may mimic folliculitis are: atopic dermatitis, whiteheads, acne, keratosis pilaris, impetigo, fire ant bites, insect bites, heat rash, contact dermatitis and dry skin.
 Folliculitis, a skin boil (Furuncle) and Carbuncle are differentiated by the symptoms and type of skin reaction as shown in this diagram. Source: John L. Bezzant, M.D.
Folliculitis, a skin boil (Furuncle) and Carbuncle are differentiated by the symptoms and type of skin reaction as shown in this diagram. Source: John L. Bezzant, M.D.To determine which of the folliculitis causes is affecting you,
your doctor may want to conduct microscopic skin and fungal tests with
potassium hydroxide, to figure out if your folliculitis is caused by a
fungus or yeast. As for skin biopsies, they are normally only done if
your folliculitis is not “typical” and is all over your body. The skin
biopsy will help rule out other possible conditions.
 Pictures of Folliculitis on legs caused by Herpes Folliculitis.
Pictures of Folliculitis on legs caused by Herpes Folliculitis. Folliculitis on Leg Caused by Bacteria such as Staphyloccocal
Folliculitis on Leg Caused by Bacteria such as StaphyloccocalFolliculitis Treatment Tips
Most mild forms of this condition will heal on their own with no
treatment. To aide healing, there are numerous folliculitis treatments,
depending on what the
caused the condition. Some of those treatments are listed below:
- Apply an antibiotic cream (mupirocin, Bactroban) or take oral antibiotics (dicolxacillin). Use anti fungal medications if prescribed.
- Over the counter antibacterial washes: benzoyl peroxide (Proactiv, Clearisil), chlorhexidine (Hibiclens folliculitis soap), phisoderm twice a day. For boils, supportive remedies such as Boil Soothe can help to relieve the puss and inflammation.
- Combine topical products with antibacterial washes.
- Soaking in warm tub of diluted white vinegar (4 parts water, 1 part vinegar)
- Soaking in warm tub with dilute Clorox bleach (full tub with ¼ cup Clorox). You can also wash your face with chlorine after shaving to kill bacteria.
- For bacterial folliculitis, use antibacterial skin washes with topical and/or oral medications. Try a shampoo that contains propylene glycol or selenium. Avoid spas or hot tubs. If using a hot tub, make sure it is properly clorinated.
- For moderate folliculitis causes and conditions, use topical antibiotic twice a day (clindamycin or metronidazole lotion). Take course (5-30 days) of oral antibiotic such as levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, cephalexin, minocycline or doxycyline. When infection clears, revert to mild antibacterial washes and topical antibiotics.
- For dry skin folliculitis, treat dryness first by using mild soapless cleansers and moisturizers like Lubriderm or Cetaphil. Other options include lactic-acid lotions (Lac-Hydrin, AmLactin for folliculitis), alpha hydroxyl acid lotions (glycolic body lotions), urea cream (Carmol 10,20,40, Urix 40) and/or salicylic acid (Salex lotion).
- For yeast or fungal based folliculitis, anti fungal shampoos/body wash (Nizoral) twice a day. The more resistant fungal folliculitis may need a topical anti fungal cream, such as Lotrimin or Lamisil and the addition of an anti fungal pill, like Difulcan.
- For folliculitis in the beard or face, a doctor may recommend that a patient not shave until the condition has healed. Use depilatory creams (hair removal) instead. Don't use depilatories more than 1x or 2x a week.
- For severe folliculitis causes and acne, the doctor may prescribe Accutane. This is off-label usage and not routine. Take care with the medication.
- Don't rub and of the papules or pustules. the bacteria or fungi can get under the fingernails and spread.
- Avoid the use of greasy cosmetics or oily skin creams. These can clog the pores.
- For scalp folliculitis use a scalp folliculitis shampoo. Keep the head as oil free and clean as possible.
In cases of hot tub dermatitis or hot tub folliculitis, treatment may not be needed as long as the condition goes away in about a week. If not visit a Doctor to determine which of the folliculitis causes triggered your skin condition.
Natural Remedies
- Take in raw garlic
- Boil Neem (Margosa) leaves in water and then use water in your bath to fight the infection. Neem has anti-bacterial properties. Consider adding some tumeric to the water.
- Ultraviolet light therapy. You can try an over-the-counter light therapy mask.
- Boost natural immunity by eating vegetables and fruits. Talk to your Doctor about dietary supplements.
- Increase water intake to 8 to 10 glasses a day. This helps to flush organisms from the body.
- Hot, moist compresses. To drain any carbuncles and boils, apply a cloth soaked in salt water (spoon 1 tsp of salt into boiling water, apply to cloth when warm). Apply for 30 minutes each day.
- Natural products such as Skin Dr. can provide added support when the skin is healing from minor skin irritations and rashes.
